- Home
- About Us
- DKPS Dealing
- BLOG
- Delhi NCR
- Delhi
- Physiotherapy at Home Near Me | Physiotherapist in South Delhi
- Best Chiropractor in Delhi
- Physiotherapist in Delhi
- Cupping Therapy in Delhi
- Home Nursing Services in Delhi
- Needle Therapy for Back Pain
- Sports Injury Physiotherapy
- Best Physiotherapist Visit at Home in Rohini Sector 24
- Physiotherapy at Home In Rohini Sector 9 |
- Physiotherapist in Pitampura | Physiotherapy at Home in Pitampura
- Physiotherapy at home in Rohini sector 29
- Physiotherapist in Paschim Vihar
- Physio home visit | Home Visit Physiotherapy |
- Physiotherapist in Saket | Best Physiotherapist in Saket |
- Physiotherapist In Janakpuri | Best Physiotherapist in Janakpuri |
- Best Physiotherapist in Punjabi Bagh | Punjabi Bagh Physiotherapist |
- Best Physiotherapist Service at Home in Dwarka, Delhi
- Best Physiotherapist in Chandigarh at Home Visit
- Faridabad
- Gurugram
- Noida
- Best Physiotherapy Gorakhpur
- Best Physiotherapist in Lucknow | Physiotherapist in Lucknow near me |
- Delhi
- Mumbai
- Delhi NCR
- Department
- Doctors
- Gallery
- Packages
- Contact Us
- Home
- About Us
- DKPS Dealing
- BLOG
- Delhi NCR
- Delhi
- Physiotherapy at Home Near Me | Physiotherapist in South Delhi
- Best Chiropractor in Delhi
- Physiotherapist in Delhi
- Cupping Therapy in Delhi
- Home Nursing Services in Delhi
- Needle Therapy for Back Pain
- Sports Injury Physiotherapy
- Best Physiotherapist Visit at Home in Rohini Sector 24
- Physiotherapy at Home In Rohini Sector 9 |
- Physiotherapist in Pitampura | Physiotherapy at Home in Pitampura
- Physiotherapy at home in Rohini sector 29
- Physiotherapist in Paschim Vihar
- Physio home visit | Home Visit Physiotherapy |
- Physiotherapist in Saket | Best Physiotherapist in Saket |
- Physiotherapist In Janakpuri | Best Physiotherapist in Janakpuri |
- Best Physiotherapist in Punjabi Bagh | Punjabi Bagh Physiotherapist |
- Best Physiotherapist Service at Home in Dwarka, Delhi
- Best Physiotherapist in Chandigarh at Home Visit
- Faridabad
- Gurugram
- Noida
- Best Physiotherapy Gorakhpur
- Best Physiotherapist in Lucknow | Physiotherapist in Lucknow near me |
- Delhi
- Mumbai
- Delhi NCR
- Department
- Doctors
- Gallery
- Packages
- Contact Us
Trochanteric Bursitis
- Home
- Trochanteric Bursitis
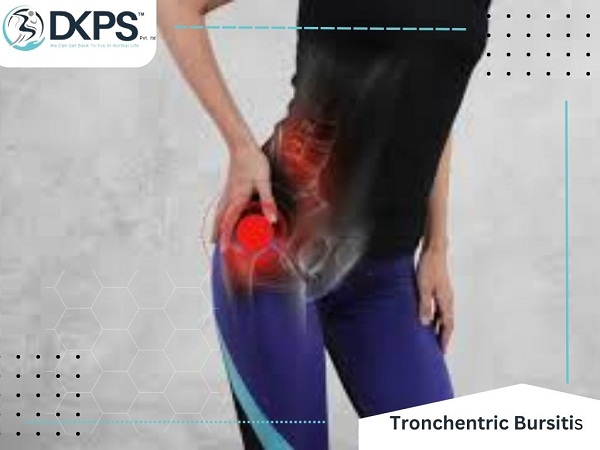
TROCHANTERIC BURSITIS
What is Trochanteric Bursitis? Trochanteric bursitis, also known as hip bursitis or greater trochanteric pain syndrome, is a common condition that affects the outer side of the hip. It occurs when the bursa, a small fluid-filled sac that acts as a cushion between bones and soft tissues, becomes inflamed and irritated. Trochanteric bursitis can cause pain and discomfort with certain movements, such as walking, running, or sitting for extended periods, and can significantly impact an individual’s daily activities and quality of life.
Causes of Trochanteric Bursitis-
The exact cause of trochanteric bursitis is not always clear, but it is commonly associated with repetitive stress, overuse, or trauma to the hip joint. Some common causes of trochanteric bursitis include:
Overuse or Repetitive Stress: Activities that involve repetitive movements of the hip joint, such as running, jumping, or prolonged sitting, can irritate the bursa and lead to inflammation.
Trauma or Injury: Direct trauma or injury to the hip, such as a fall, can cause the bursa to become inflamed.
Muscle Imbalances or Weakness: Imbalances or weakness in the muscles around the hip, particularly the gluteal muscles, can alter the biomechanics of the hip joint, leading to increased stress on the bursa and potential inflammation.
Structural Abnormalities: Certain structural abnormalities of the hip, such as hip dysplasia or leg length discrepancy, can increase the risk of trochanteric bursitis.
Medical Conditions: Certain medical conditions, such as rheumatoid arthritis, gout, or hip osteoarthritis, can also increase the risk of developing trochanteric bursitis.
Symptoms of Trochanteric Bursitis
Trochanteric bursitis typically presents with pain and tenderness over the outer side of the hip, specifically around the bony prominence called the greater trochanter. The pain may be sharp, aching, or burning in nature and may worsen with certain activities, such as walking, running, or lying on the affected side. Other common symptoms of trochanteric bursitis include:
Swelling or Redness: The affected area may be swollen or red due to inflammation of the bursa.
Pain with Pressure: The pain may worsen when direct pressure is applied to the greater trochanter, such as when lying on the affected side or sitting for extended periods.
Additional Links
For More Articles
DKPS Physiotherapy services at Home
DWARKA | PASCHIM VIHAR | PEERAGARHI | VIKASPURI | PITAMPURA | KOHAT ENCLAVE | RANI BAGH | ROHINI | JANAKPURI | MANGOLPURI | PUNJABI BAGH | NANGLOI | BAHADURGARH | NOIDA | GREATER NOIDA| GHAZIABAD | GURGAON | FARIDABAD | MUMBAI | GORAKHPUR | LUCKNOW | CHANDIGARH |
