- Home
- About Us
- DKPS Dealing
- BLOG
- Delhi NCR
- Delhi
- Physiotherapy at Home Near Me | Physiotherapist in South Delhi
- Best Chiropractor in Delhi
- Physiotherapist in Delhi
- Cupping Therapy in Delhi
- Home Nursing Services in Delhi
- Needle Therapy for Back Pain
- Sports Injury Physiotherapy
- Best Physiotherapist Visit at Home in Rohini Sector 24
- Physiotherapy at Home In Rohini Sector 9 |
- Physiotherapist in Pitampura | Physiotherapy at Home in Pitampura
- Physiotherapy at home in Rohini sector 29
- Physiotherapist in Paschim Vihar
- Physio home visit | Home Visit Physiotherapy |
- Physiotherapist in Saket | Best Physiotherapist in Saket |
- Physiotherapist In Janakpuri | Best Physiotherapist in Janakpuri |
- Best Physiotherapist in Punjabi Bagh | Punjabi Bagh Physiotherapist |
- Best Physiotherapist Service at Home in Dwarka, Delhi
- Best Physiotherapist in Chandigarh at Home Visit
- Faridabad
- Gurugram
- Noida
- Best Physiotherapy Gorakhpur
- Best Physiotherapist in Lucknow | Physiotherapist in Lucknow near me |
- Delhi
- Mumbai
- Delhi NCR
- Department
- Doctors
- Gallery
- Packages
- Contact Us
- Home
- About Us
- DKPS Dealing
- BLOG
- Delhi NCR
- Delhi
- Physiotherapy at Home Near Me | Physiotherapist in South Delhi
- Best Chiropractor in Delhi
- Physiotherapist in Delhi
- Cupping Therapy in Delhi
- Home Nursing Services in Delhi
- Needle Therapy for Back Pain
- Sports Injury Physiotherapy
- Best Physiotherapist Visit at Home in Rohini Sector 24
- Physiotherapy at Home In Rohini Sector 9 |
- Physiotherapist in Pitampura | Physiotherapy at Home in Pitampura
- Physiotherapy at home in Rohini sector 29
- Physiotherapist in Paschim Vihar
- Physio home visit | Home Visit Physiotherapy |
- Physiotherapist in Saket | Best Physiotherapist in Saket |
- Physiotherapist In Janakpuri | Best Physiotherapist in Janakpuri |
- Best Physiotherapist in Punjabi Bagh | Punjabi Bagh Physiotherapist |
- Best Physiotherapist Service at Home in Dwarka, Delhi
- Best Physiotherapist in Chandigarh at Home Visit
- Faridabad
- Gurugram
- Noida
- Best Physiotherapy Gorakhpur
- Best Physiotherapist in Lucknow | Physiotherapist in Lucknow near me |
- Delhi
- Mumbai
- Delhi NCR
- Department
- Doctors
- Gallery
- Packages
- Contact Us
Hip Osteoarthritis
- Home
- Hip Osteoarthritis
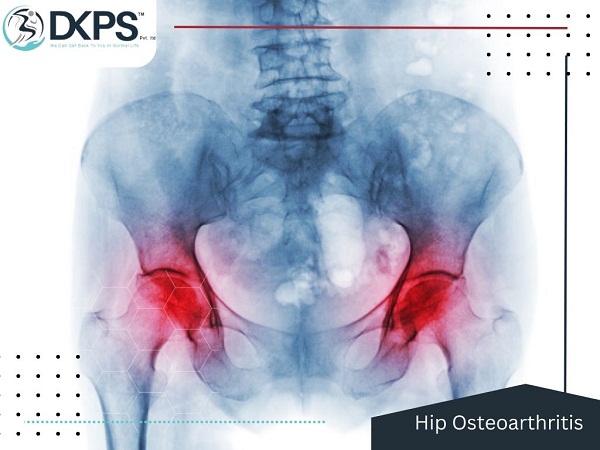
Hip Osteoarthritis
Hip Osteoarthritis: Understanding the Causes, Symptoms, Diagnosis, and Treatment Osteoarthritis, commonly referred to as “wear and tear” arthritis, is a degenerative joint disease that affects millions of people worldwide. It can occur in any joint in the body, including the hip joint, which is a critical weight-bearing joint that allows for movement and mobility. Hip osteoarthritis is a chronic condition that causes the cartilage in the hip joint to gradually break down, resulting in pain, stiffness, and reduced function. In this article, we will delve into the causes, symptoms, diagnosis, and treatment of hip osteoarthritis.
Causes of Hip Osteoarthritis:
The exact cause of hip osteoarthritis is not fully understood, but there are several risk factors that can contribute to its development, including:
Age: Hip osteoarthritis is more common in older individuals, as the wear and tear on the joint accumulate over time.
Genetics: There is evidence to suggest that genetics play a role in the development of hip osteoarthritis. If you have a family history of osteoarthritis, you may be at a higher risk of developing the condition.
Previous joint injuries: Previous injuries to the hip joint, such as fractures or dislocations, can increase the risk of developing hip osteoarthritis later in life.
Joint abnormalities: Certain joint abnormalities, such as hip dysplasia or femoroacetabular impingement (FAI), can cause abnormal wear and tear on the hip joint, leading to osteoarthritis.
Obesity: Excess weight places additional stress on the hip joint, increasing the risk of hip osteoarthritis.
Overuse or repetitive stress: Overuse or repetitive stress on the hip joint, such as from certain sports or occupations, can accelerate the breakdown of cartilage and lead to hip osteoarthritis.
Symptoms of Hip Osteoarthritis:
The symptoms of hip osteoarthritis can vary from person to person, but common signs and symptoms may include:
Pain: Hip pain is the hallmark symptom of hip osteoarthritis. The pain is usually felt in the groin area, but it can also radiate to the buttocks, thigh, or knee. The pain may be mild to severe and may worsen with weight-bearing activities such as walking, standing, or climbing stairs.
Stiffness: Hip osteoarthritis can cause stiffness in the hip joint, making it difficult to move the joint freely. Stiffness is typically worse in the morning or after prolonged periods of inactivity and may improve with movement.
Reduced range of motion: As hip osteoarthritis progresses, the range of motion in the hip joint may become limited. This can make it challenging to perform activities that require a wide range of hip motions, such as bending, squatting, or twisting.
Swelling and tenderness: In some cases, hip osteoarthritis may cause swelling and tenderness around the hip joint. The joint may also feel warm to the touch.
Joint instability: Hip osteoarthritis can cause the hip joint to feel unstable or give way, making it difficult to bear weight or move around confidently.
Diagnosis of Hip Osteoarthritis:
If you are experiencing symptoms suggestive of hip osteoarthritis, it is essential to see a healthcare professional for an accurate diagnosis. The diagnosis of hip osteoarthritis typically involves the following:
Medical history and physical examination: Your healthcare provider will take a detailed medical history, including information about your symptoms, previous injuries, and family history of osteoarthritis. A physical examination will be conducted to assess the range of motion, stability, and tenderness of the hip joint.
Imaging tests: X-rays are often the first imaging tests ordered to visualize the hip joint and assess for signs of osteoarthritis. X-rays can show the narrowing of the joint space, changes in the shape of the bones, and the presence of bone spurs, which are common findings in hip osteoarthritis. Other imaging tests such as magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) or computed tomography (CT) scans may be ordered in some cases to get a more detailed view of the joint and rule out other conditions.
Joint aspiration: In some cases, your healthcare provider may perform a joint aspiration, which involves removing a small sample of joint fluid from the hip joint using a needle. The fluid can be analyzed to rule out other causes of joint pain, such as infection or inflammation.
Clinical assessment tools: Your healthcare provider may also use clinical assessment tools, such as questionnaires or scoring systems, to evaluate the severity of your hip osteoarthritis and monitor your symptoms over time.
Treatment of Hip Osteoarthritis:
The treatment approach for hip osteoarthritis typically involves a combination of conservative measures and, in some cases, surgical intervention. The treatment plan is tailored to the individual needs of the patient and may include the following:
Lifestyle modifications: Lifestyle modifications can help manage the symptoms of hip osteoarthritis and slow down the progression of the disease. These may include weight loss, regular exercise, avoiding activities that worsen hip pain, using assistive devices such as canes or crutches, and modifying activities to reduce stress on the hip joint.
Medications: Over-the-counter pain medications such as acetaminophen or nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs) may be recommended to relieve pain and reduce inflammation. Topical pain creams or gels may also be used. In some cases, your healthcare provider may prescribe stronger pain medications or corticosteroid injections for more severe pain.
Physical therapy: Physical therapy can help improve hip joint flexibility, strength, and stability. A physical therapist can provide exercises, stretches, and other modalities to help manage hip osteoarthritis symptoms and improve overall hip joint function.
Assistive devices: The use of assistive devices, such as canes, crutches, or braces, can help reduce the load on the hip joint and improve mobility.
Joint injections: In some cases, your healthcare provider may recommend joint injections of corticosteroids or hyaluronic acid to help reduce pain and inflammation in the hip joint.
Alternative therapies: Some patients may find relief from hip osteoarthritis symptoms through alternative therapies such as acupuncture, chiropractic care, or herbal supplements. However, it’s important to discuss these options with your healthcare provider before trying them.
Surgical intervention: If conservative measures are not effective in managing the symptoms of hip osteoarthritis, your healthcare provider may recommend surgical intervention. There are several surgical options available, including joint preservation surgeries such as arthroscopy or joint replacement surgeries such as total hip replacement. The choice of surgery depends on various factors, including the severity of hip osteoarthritis, ag…
How https://drsinghphysiocare.com/Can Help You:-
Drsinghphysiocare.com has very experienced physiotherapists well-versed in modern manual techniques and rehabilitation protocols. Moving patients from one place to another is complicated and can even increase the damage. Drsinghphysiocare.com offers physiotherapists home visits to rehabilitate patients in the comfort of their homes. Regular home physiotherapy by our physiotherapist helps patients actively and vigorously return to independence.
Senior physicians select our talented and experienced physiotherapists after they meet our strict recruitment standards. As a result of our higher standards and quality of service, many patients have recovered from the comfort of their homes and saved their valuable time and money.
For More details kindly visit on –
https://drsinghphysiocare.com/
https://drsinghphysiocare.com/delhi/
https://drsinghphysiocare.com/mumbai/
https://drsinghphysiocare.com/physiotherapy-at-home-near-me-physiotherapist-in-south-delhi/
Additional Links
For More Articles
DKPS Physiotherapy services at Home
DWARKA | PASCHIM VIHAR | PEERAGARHI | VIKASPURI | PITAMPURA | KOHAT ENCLAVE | RANI BAGH | ROHINI | JANAKPURI | MANGOLPURI | PUNJABI BAGH | NANGLOI | BAHADURGARH | NOIDA | GREATER NOIDA| GHAZIABAD | GURGAON | FARIDABAD | MUMBAI | GORAKHPUR | LUCKNOW | CHANDIGARH |
