- Home
- About Us
- DKPS Dealing
- BLOG
- Delhi NCR
- Delhi
- Physiotherapy at Home Near Me | Physiotherapist in South Delhi
- Best Chiropractor in Delhi
- Physiotherapist in Delhi
- Cupping Therapy in Delhi
- Home Nursing Services in Delhi
- Needle Therapy for Back Pain
- Sports Injury Physiotherapy
- Best Physiotherapist Visit at Home in Rohini Sector 24
- Physiotherapy at Home In Rohini Sector 9 |
- Physiotherapist in Pitampura | Physiotherapy at Home in Pitampura
- Physiotherapy at home in Rohini sector 29
- Physiotherapist in Paschim Vihar
- Physio home visit | Home Visit Physiotherapy |
- Physiotherapist in Saket | Best Physiotherapist in Saket |
- Physiotherapist In Janakpuri | Best Physiotherapist in Janakpuri |
- Best Physiotherapist in Punjabi Bagh | Punjabi Bagh Physiotherapist |
- Best Physiotherapist Service at Home in Dwarka, Delhi
- Best Physiotherapist in Chandigarh at Home Visit
- Faridabad
- Gurugram
- Noida
- Best Physiotherapy Gorakhpur
- Best Physiotherapist in Lucknow | Physiotherapist in Lucknow near me |
- Delhi
- Mumbai
- Delhi NCR
- Department
- Doctors
- Gallery
- Packages
- Contact Us
- Home
- About Us
- DKPS Dealing
- BLOG
- Delhi NCR
- Delhi
- Physiotherapy at Home Near Me | Physiotherapist in South Delhi
- Best Chiropractor in Delhi
- Physiotherapist in Delhi
- Cupping Therapy in Delhi
- Home Nursing Services in Delhi
- Needle Therapy for Back Pain
- Sports Injury Physiotherapy
- Best Physiotherapist Visit at Home in Rohini Sector 24
- Physiotherapy at Home In Rohini Sector 9 |
- Physiotherapist in Pitampura | Physiotherapy at Home in Pitampura
- Physiotherapy at home in Rohini sector 29
- Physiotherapist in Paschim Vihar
- Physio home visit | Home Visit Physiotherapy |
- Physiotherapist in Saket | Best Physiotherapist in Saket |
- Physiotherapist In Janakpuri | Best Physiotherapist in Janakpuri |
- Best Physiotherapist in Punjabi Bagh | Punjabi Bagh Physiotherapist |
- Best Physiotherapist Service at Home in Dwarka, Delhi
- Best Physiotherapist in Chandigarh at Home Visit
- Faridabad
- Gurugram
- Noida
- Best Physiotherapy Gorakhpur
- Best Physiotherapist in Lucknow | Physiotherapist in Lucknow near me |
- Delhi
- Mumbai
- Delhi NCR
- Department
- Doctors
- Gallery
- Packages
- Contact Us
Hip Impingement
- Home
- Hip Impingement
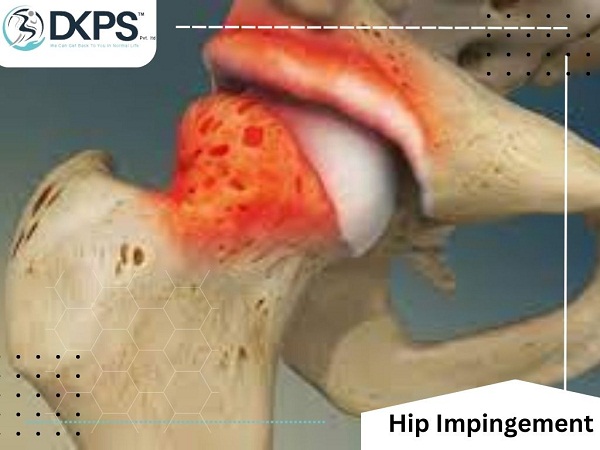
Hip Impingement
Hip Impingement: Causes, Symptoms, Diagnosis, and Treatment
The hip joint is a crucial joint that allows for smooth movement and weight-bearing of the lower body. However, certain conditions can disrupt the normal function of the hip joint, leading to pain, discomfort, and reduced mobility. One such condition is hip impingement, also known as Femoroacetabular impingement (FAI). In this article, we will explore hip impingement in detail, including its causes, symptoms, diagnosis, and treatment options.
What is Hip Impingement?
Hip impingement, or FAI, is a condition where there is abnormal contact between the femoral head (the ball-shaped part of the thigh bone) and the acetabulum (the socket of the hip joint) during hip movements. This abnormal contact can result in friction, irritation, and damage to the joint surfaces, leading to pain, inflammation, and reduced range of motion.
fore more details visit on-
https://drsinghphysiocare.com/p
Hip impingement can occur in three different types, namely:
Cam impingement: In this type, there is an abnormality in the shape of the femoral head, causing it to be misshapen or not perfectly round. This can result in uneven contact with the acetabulum during hip movements, leading to impingement.
Pincer impingement: In this type, there is an abnormality in the shape of the acetabulum, causing it to cover more of the femoral head than normal. This excessive coverage can lead to impingement as the femoral head contacts the acetabulum during hip movements.
Mixed impingement: This type involves a combination of both cam and pincer impingements.
Causes of Hip Impingement
Hip impingement can occur due to various factors, including anatomical abnormalities, repetitive trauma, or developmental issues. Some of the common causes of hip impingement include:
Anatomical Abnormalities: Certain structural abnormalities in the hip joint can increase the risk of hip impingement. For example, individuals with a misshapen femoral head, a deep acetabulum, or an abnormal angle between the femoral neck and shaft may be more prone to hip impingement.
Repetitive Trauma: Engaging in activities that involve repetitive hip motions, such as running, jumping, or twisting, can increase the risk of hip impingement. These repetitive motions can cause wear and tear on the hip joint, leading to impingement over time.
Developmental Issues: Some individuals may develop hip impingement due to developmental issues during growth and development. For example, a condition called slipped capital femoral epiphysis (SCFE), where the growth plate of the femoral head slips, can result in hip impingement.
Genetic Factors: There may be a genetic predisposition to hip impingement, as certain genetic factors may influence the development of the hip joint during fetal development, leading to an increased risk of impingement later in life.
Symptoms of Hip Impingement
The symptoms of hip impingement can vary depending on the severity of the condition and the individual. However, common symptoms of hip impingement may include:
Hip Pain: Pain is the most common symptom of hip impingement. The pain is typically located in the groin area, but it can also be felt in the hip, buttocks, or thigh. The pain may be sharp, stabbing, or aching in nature, and it may worsen with hip movements, prolonged sitting or standing, or engaging in activities that involve repetitive hip motions.
Limited Range of Motion: Hip impingement can result in a reduced range of motion in the hip joint. Stiffness: Stiffness in the hip joint may be experienced, making it difficult to perform certain activities that require hip mobility, such as squatting, bending, or twisting.
Clicking or Snapping Sensation: Some individuals with hip impingement may experience clicking or snapping sensations in the hip joint during movements, such as walking or rotating the hip. This may be caused by the abnormal contact between the femoral head and the acetabulum.
Muscle Weakness: Hip impingement can cause muscle weakness in the hip and surrounding areas, as the pain and limited range of motion may result in reduced use and function of the hip muscles.
Pain with Sitting or Driving: Sitting for prolonged periods of time or driving for long distances may exacerbate the hip impingement pain due to increased pressure on the hip joint.
It is important to note that the severity of symptoms can vary among individuals, and some individuals with hip impingement may not experience any symptoms at all. However, if you suspect you may have hip impingement or are experiencing any of the above symptoms, it is important to consult a healthcare professional for proper evaluation and diagnosis.
Diagnosis of Hip Impingement
Diagnosing hip impingement typically involves a comprehensive evaluation by a healthcare professional, which may include:
Medical History and Physical Examination: Your healthcare provider will likely take a detailed medical history, including any previous injuries, family history, and current symptoms. A physical examination will be conducted, which may involve assessing the range of motion of the hip joint, checking for pain or tenderness, and evaluating for any muscle weakness or imbalances.
Imaging Tests: Imaging tests, such as X-rays, magnetic resonance imaging (MRI), or computed tomography (CT) scans, may be ordered to obtain detailed images of the hip joint. These tests can help identify any structural abnormalities, such as a misshapen femoral head, deep acetabulum, or abnormal angles, that may be indicative of hip impingement.
Diagnostic Hip Injection: In some cases, a diagnostic hip injection may be performed to confirm the diagnosis of hip impingement. A numbing medication is injected into the hip joint, and if the pain is significantly reduced or eliminated after the injection, it may suggest that the impingement is the source of the pain.
Treatment Options for Hip Impingement
The treatment approach for hip impingement depends on the severity of the condition, the age and activity level of the individual, and the presence of any associated hip joint damage. The main goal of treatment is to relieve pain, improve hip function, and prevent further damage to the hip joint. Treatment options for hip impingement may include:
Conservative Management: Conservative management options may be recommended initially for mild to moderate cases of hip impingement. This may include:
Rest: Avoiding activities that exacerbate the hip impingement pain and providing adequate rest to the hip joint can help reduce inflammation and promote healing.
Medications: Nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs), such as ibuprofen or naproxen, may be prescribed to relieve pain and reduce inflammation.
Physical Therapy: Physical therapy may be recommended to strengthen the hip muscles, improve hip stability, and promote better hip mechanics. This may include exercises to improve the hip range of motion, strengthen hip muscles, and correct any muscle imbalances or weaknesses.
Activity Modification: Modifying activities that involve repetitive hip motions, such as running or jumping, may be necessary to reduce stress on the hip joint and prevent further impingement.
Injections: Corticosteroid injections may be used to reduce pain and inflammation in the hip joint. These injections are typically performed under guidance using imaging techniques such as ultrasound or fluoroscopy to ensure precise placement of the medication into the affected area.
Lifestyle Changes: Making lifestyle changes, such as maintaining a healthy body weight, avoiding activities that exacerbate hip impingement, and improving hip mechanics during activities, can help reduce stress on the hip joint and prevent further damage.
Surgical Interventions: In cases where conservative management fails to provide relief or in severe cases of hip impingement with significant damage to the hip joint, surgical intervention may be necessary. There are two main types of surgical procedures that may be considered:
Arthroscopic Surgery: Arthroscopic surgery is a minimally invasive procedure that uses small incisions and a camera-guided instrument to remove excess bone or repair damaged tissues in the hip joint. This procedure may be recommended for mild to moderate cases of hip impingement.
Open Surgery: In more severe cases of hip impingement with significant damage to the hip joint, open surgery may be necessary. This involves a larger incision and more extensive surgical intervention, such as reshaping the femoral head or acetabulum, repairing damaged labrum or cartilage, or addressing any other structural abnormalities in the hip joint.
Rehabilitation and Recovery
Rehabilitation and recovery following surgical intervention for hip impingement typically involve a comprehensive rehabilitation program that may include:
Physical Therapy: Physical therapy plays a crucial role in the recovery process after hip impingement surgery. It may involve exercises to improve hip strength, flexibility, and range of motion, as well as gait training, functional activities, and pain management techniques.
Gradual Return to Activities: Depending on the severity of the hip impingement and the type of surgical procedure performed, the timeline for returning to normal activities may vary. It is essential to follow the guidance of your healthcare provider and physical therapist to gradually resume activities and avoid activities that may stress the hip joint too soon.
Lifestyle Modifications: Lifestyle modifications, such as maintaining a healthy body weight, avoiding high-impact activities, and practicing proper hip mechanics during activities, may be necessary to prevent the recurrence of hip impingement and promote long-term hip joint health.
Pain Management: Pain management techniques, such as medications or local modalities such as ice or heat, may be used to manage pain during the recovery process.
Regular Follow-up with Healthcare Provider: Regular follow-up visits with your healthcare provider are essential to monitor your progress, address any concerns or complications, and make necessary adjustments to your rehabilitation program.
Conclusion
Hip impingement is a common condition that can cause pain, discomfort, and reduced hip function. It can affect individuals of all ages and activity levels, and early diagnosis and treatment are crucial in preventing further damage to the hip joint. If you suspect you may have hip impingement or are experiencing symptoms such as hip pain, limited range of motion, or stiffness, it is important to consult a healthcare professional for proper evaluation and management.
Treatment for hip impingement may include conservative management options such as rest, medications, physical therapy, and activity modification. In more severe cases, surgical intervention may be necessary, and rehabilitation following surgery plays a critical role in the recovery process. Lifestyle modifications and regular follow-up visits with healthcare providers are essential in preventing recurrence and promoting long-term hip joint health.
With proper diagnosis, treatment, and rehabilitation, most individuals with hip impingement can achieve significant pain relief, improved hip function, and a return to their desired activities. If you suspect you may have hip impingement, seek medical attention and work with your healthcare provider and physical therapist to develop an individualized treatment plan for optimal outcomes.
How Drsinghphysiocare Can Help You:-
Drsinghphysiocare.com has very experienced physiotherapists well-versed in modern manual techniques and rehabilitation protocols. Moving patients from one place to another is complicated and can even increase the damage. Drsinghphysiocare.com offers physiotherapists home visits to rehabilitate patients in the comfort of their homes. Regular home physiotherapy by our physiotherapist helps patients actively and vigorously return to independence.
Senior physicians select our talented and experienced physiotherapists after they meet our strict recruitment standards. As a result of our higher standards and quality of service, many patients have recovered from the comfort of their homes and saved their valuable time and money
Additional Links
For More Articles
DKPS Physiotherapy services at Home
DWARKA | PASCHIM VIHAR | PEERAGARHI | VIKASPURI | PITAMPURA | KOHAT ENCLAVE | RANI BAGH | ROHINI | JANAKPURI | MANGOLPURI | PUNJABI BAGH | NANGLOI | BAHADURGARH | NOIDA | GREATER NOIDA| GHAZIABAD | GURGAON | FARIDABAD | MUMBAI | GORAKHPUR | LUCKNOW | CHANDIGARH |
