- Home
- About Us
- DKPS Dealing
- BLOG
- Delhi NCR
- Delhi
- Physiotherapy at Home Near Me | Physiotherapist in South Delhi
- Best Chiropractor in Delhi
- Physiotherapist in Delhi
- Cupping Therapy in Delhi
- Home Nursing Services in Delhi
- Needle Therapy for Back Pain
- Sports Injury Physiotherapy
- Best Physiotherapist Visit at Home in Rohini Sector 24
- Physiotherapy at Home In Rohini Sector 9 |
- Physiotherapist in Pitampura | Physiotherapy at Home in Pitampura
- Physiotherapy at home in Rohini sector 29
- Physiotherapist in Paschim Vihar
- Physio home visit | Home Visit Physiotherapy |
- Physiotherapist in Saket | Best Physiotherapist in Saket |
- Physiotherapist In Janakpuri | Best Physiotherapist in Janakpuri |
- Best Physiotherapist in Punjabi Bagh | Punjabi Bagh Physiotherapist |
- Best Physiotherapist Service at Home in Dwarka, Delhi
- Best Physiotherapist in Chandigarh at Home Visit
- Faridabad
- Gurugram
- Noida
- Best Physiotherapy Gorakhpur
- Best Physiotherapist in Lucknow | Physiotherapist in Lucknow near me |
- Delhi
- Mumbai
- Delhi NCR
- Department
- Doctors
- Gallery
- Packages
- Contact Us
- Home
- About Us
- DKPS Dealing
- BLOG
- Delhi NCR
- Delhi
- Physiotherapy at Home Near Me | Physiotherapist in South Delhi
- Best Chiropractor in Delhi
- Physiotherapist in Delhi
- Cupping Therapy in Delhi
- Home Nursing Services in Delhi
- Needle Therapy for Back Pain
- Sports Injury Physiotherapy
- Best Physiotherapist Visit at Home in Rohini Sector 24
- Physiotherapy at Home In Rohini Sector 9 |
- Physiotherapist in Pitampura | Physiotherapy at Home in Pitampura
- Physiotherapy at home in Rohini sector 29
- Physiotherapist in Paschim Vihar
- Physio home visit | Home Visit Physiotherapy |
- Physiotherapist in Saket | Best Physiotherapist in Saket |
- Physiotherapist In Janakpuri | Best Physiotherapist in Janakpuri |
- Best Physiotherapist in Punjabi Bagh | Punjabi Bagh Physiotherapist |
- Best Physiotherapist Service at Home in Dwarka, Delhi
- Best Physiotherapist in Chandigarh at Home Visit
- Faridabad
- Gurugram
- Noida
- Best Physiotherapy Gorakhpur
- Best Physiotherapist in Lucknow | Physiotherapist in Lucknow near me |
- Delhi
- Mumbai
- Delhi NCR
- Department
- Doctors
- Gallery
- Packages
- Contact Us
Boutonniere deformity
- Home
- Boutonniere deformity
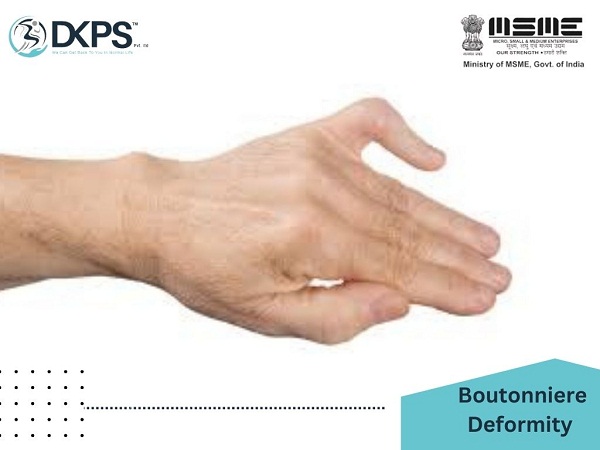
Boutonniere deformity
Boutonniere deformity is a condition that affects the fingers, particularly the middle joint of the finger. It is characterized by the inability to straighten the finger due to damage to the tendon and ligaments that support the joint. The condition is also known as “buttonhole deformity” or “central slip injury” and can occur as a result of trauma, rheumatoid arthritis, or other medical conditions. In this article, we will discuss the causes, symptoms, diagnosis, treatment, and exercises that can help with boutonniere deformity.
Causes of Boutonniere Deformity
Boutonniere deformity can be caused by a variety of factors, including:
Trauma – The most common cause of boutonniere deformity is trauma to the finger, such as a direct blow, a laceration, or a crush injury. This can damage the tendon and ligaments that support the middle joint of the finger, leading to deformity.
Rheumatoid Arthritis – Rheumatoid arthritis is a chronic autoimmune disorder that causes inflammation and damage to the joints. It can also affect the tendons and ligaments that support the fingers, leading to boutonniere deformity.
Other Medical Conditions – Boutonniere deformity can also be caused by other medical conditions, such as systemic lupus erythematosus, psoriatic arthritis, and gout.
Symptoms of Boutonniere Deformity
The symptoms of boutonniere deformity include:
Inability to Straighten the Finger –
The most noticeable symptom of boutonniere deformity is the inability to straighten the middle joint of the finger. This is because the tendon and ligaments that support the joint have been damaged.
Swelling – The affected finger may also become swollen due to the inflammation caused by the injury or underlying medical condition.
Pain – Pain in the affected finger may be present, especially if the deformity is caused by trauma.
Redness – The skin around the affected joint may become red due to inflammation.
Diagnosis of Boutonniere Deformity
Boutonniere deformity is diagnosed through a physical examination by a healthcare professional, such as a hand surgeon or orthopedic specialist. During the examination, the healthcare professional will assess the range of motion in the finger, the extent of the deformity, and any pain or discomfort.
Imaging tests, such as X-rays, may also be ordered to evaluate the extent of the injury and to rule out other medical conditions that may be causing the symptoms.
Treatment of Boutonniere Deformity
The treatment of boutonniere deformity depends on the severity of the injury and the underlying cause. In mild cases, non-surgical treatment may be recommended, while more severe cases may require surgery.
Non-Surgical Treatment –
Non-surgical treatment for boutonniere deformity may include:
a. Splinting – Splinting the affected finger in a straight position can help to prevent further damage and promote healing.
b. Physical Therapy – Physical therapy may be recommended to help restore the range of motion in the finger and strengthen the surrounding muscles.
c. Medications – Nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs) may be prescribed to help reduce pain and inflammation.
Surgical Treatment – If non-surgical treatment is not effective or if the deformity is severe, surgery may be recommended. The type of surgery will depend on the extent of the injury and the underlying cause of the deformity. Surgery may involve repairing the damaged tendon or ligament or fusing the affected joint to promote stability.
Exercises for Boutonniere Deformity-
Physical therapy exercises can play an important role in the non-surgical treatment of boutonniere deformity. These exercises can help to improve the range of motion in the finger, strengthen the surrounding muscles, and prevent further damage to the joint. Here are some exercises that may be recommended by a physical therapist:
Finger Extensions – This exercise involves straightening the fingers as much as possible and holding the position for a few seconds before slowly releasing. It can help to improve the range of motion in the finger and prevent further deformity.
Finger Flexion – This exercise involves bending the fingers as much as possible and holding the position for a few seconds before slowly releasing it. It can help to improve flexibility in the finger and prevent stiffness.
Hand Gripping – This exercise involves squeezing a small ball or hand gripper for a few seconds before slowly releasing it. It can help strengthen the hand muscles and improve grip strength.
Wrist Rotation – This exercise involves rotating the wrist in a circular motion, first clockwise and then counterclockwise. It can help to improve flexibility in the wrist and prevent stiffness.
Hand Stretching – This exercise involves stretching the hand by placing the palm against a flat surface and gently pushing the fingers back toward the wrist. It can help to improve flexibility in the hand and prevent stiffness.
It is important to perform these exercises under the guidance of a physical therapist to ensure that they are done safely and effectively. The therapist may also recommend other exercises and modifications based on the individual needs of the patient.
How Physiotherapy Can Help in Boutonniere Deformity-
Resting the Finger – Resting the affected finger can help to reduce pain and inflammation and promote healing. It is important to avoid any activities that may aggravate the condition, such as gripping or twisting motions.
Applying Ice By DKPS Professionals – Applying ice to the affected area can help to reduce swelling and numb pain. Ice should be used for 20 minutes, several times a day, and wrapped in a towel or cloth to avoid skin damage.
Using Splints or Braces – Splints or braces can help to immobilize the affected finger and prevent further deformity. They may be recommended by a physical therapist or healthcare provider.
Taking Anti-inflammatory Medications – Nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory medications (NSAIDs) can help to reduce pain and inflammation in the affected finger. They should only be taken under the guidance of a healthcare provider.
Practicing Good Hand Hygiene – Practicing good hand hygiene, such as washing your hands regularly and avoiding touching your face, can help to prevent infection in the affected finger.
In conclusion, boutonniere deformity is a condition that can significantly impact hand function and quality of life. However, with early diagnosis and appropriate treatment, it is often possible to improve the range of motion, reduce pain and inflammation, and prevent further deformity. Physiotherapy can play an important role in the management of this condition, providing a range of techniques and interventions to promote healing, improve range of motion, reduce pain and inflammation, and strengthen muscles. If you are experiencing any symptoms of boutonniere deformity, it is important to seek medical attention right away to get the help you need.
How Drsinghphysiocare Can Help You:-
Drsinghphysiocare.com has very experienced physiotherapists well-versed in modern manual techniques and rehabilitation protocols. Moving patients from one place to another is complicated and can even increase the damage. Drsinghphysiocare.com offers physiotherapists home visits to rehabilitate patients in the comfort of their homes. Regular home physiotherapy by our physiotherapist helps patients actively and vigorously return to independence.
Senior physicians select our talented and experienced physiotherapists after they meet our strict recruitment standards. As a result of our higher standards and quality of service, many patients have recovered from the comfort of their homes and saved their valuable time and money.
For More Article-
Physiotherapy/ Chiropractor/Cupping therapy/Dry Needling therapy services available in –
Check Professionals details at location wise –
WEST DELHI | VIKASPURI | JANAKPURI | RAJOURI GARDEN PASCHIM VIHAR| PANJABI BAGH| PITAMPURA| DWARKA ALL SECTOR | TILAK NAGAR| SUBHAS NAGAR| MAHAVIR ENCLAVE ,| UTTAM NAGAR,| NAWADA,| NAJAFGARH,| INDERLOK, TRINAGAR | RAJA GARDEN | SAGARPUR | DELHI CANTT| NARAYANA | MOTI NAGAR|Mumbai | Lucknow | Gorakhpur | Guwahati | Pune| Bangalore | Goa | Faridabad | Noida | Greater Noida | Mathura | Vrindavan | Kanpur | Jaipur | Hyderabad | Delhi |
Additional Links
For More Articles
DKPS Physiotherapy services at Home
DWARKA | PASCHIM VIHAR | PEERAGARHI | VIKASPURI | PITAMPURA | KOHAT ENCLAVE | RANI BAGH | ROHINI | JANAKPURI | MANGOLPURI | PUNJABI BAGH | NANGLOI | BAHADURGARH | NOIDA | GREATER NOIDA| GHAZIABAD | GURGAON | FARIDABAD | MUMBAI | GORAKHPUR | LUCKNOW | CHANDIGARH |
