- Home
- About Us
- DKPS Dealing
- BLOG
- Delhi NCR
- Delhi
- Physiotherapy at Home Near Me | Physiotherapist in South Delhi
- Best Chiropractor in Delhi
- Physiotherapist in Delhi
- Cupping Therapy in Delhi
- Home Nursing Services in Delhi
- Needle Therapy for Back Pain
- Sports Injury Physiotherapy
- Best Physiotherapist Visit at Home in Rohini Sector 24
- Physiotherapy at Home In Rohini Sector 9 |
- Physiotherapist in Pitampura | Physiotherapy at Home in Pitampura
- Physiotherapy at home in Rohini sector 29
- Physiotherapist in Paschim Vihar
- Physio home visit | Home Visit Physiotherapy |
- Physiotherapist in Saket | Best Physiotherapist in Saket |
- Physiotherapist In Janakpuri | Best Physiotherapist in Janakpuri |
- Best Physiotherapist in Punjabi Bagh | Punjabi Bagh Physiotherapist |
- Best Physiotherapist Service at Home in Dwarka, Delhi
- Best Physiotherapist in Chandigarh at Home Visit
- Faridabad
- Gurugram
- Noida
- Best Physiotherapy Gorakhpur
- Best Physiotherapist in Lucknow | Physiotherapist in Lucknow near me |
- Delhi
- Mumbai
- Delhi NCR
- Department
- Doctors
- Gallery
- Packages
- Contact Us
- Home
- About Us
- DKPS Dealing
- BLOG
- Delhi NCR
- Delhi
- Physiotherapy at Home Near Me | Physiotherapist in South Delhi
- Best Chiropractor in Delhi
- Physiotherapist in Delhi
- Cupping Therapy in Delhi
- Home Nursing Services in Delhi
- Needle Therapy for Back Pain
- Sports Injury Physiotherapy
- Best Physiotherapist Visit at Home in Rohini Sector 24
- Physiotherapy at Home In Rohini Sector 9 |
- Physiotherapist in Pitampura | Physiotherapy at Home in Pitampura
- Physiotherapy at home in Rohini sector 29
- Physiotherapist in Paschim Vihar
- Physio home visit | Home Visit Physiotherapy |
- Physiotherapist in Saket | Best Physiotherapist in Saket |
- Physiotherapist In Janakpuri | Best Physiotherapist in Janakpuri |
- Best Physiotherapist in Punjabi Bagh | Punjabi Bagh Physiotherapist |
- Best Physiotherapist Service at Home in Dwarka, Delhi
- Best Physiotherapist in Chandigarh at Home Visit
- Faridabad
- Gurugram
- Noida
- Best Physiotherapy Gorakhpur
- Best Physiotherapist in Lucknow | Physiotherapist in Lucknow near me |
- Delhi
- Mumbai
- Delhi NCR
- Department
- Doctors
- Gallery
- Packages
- Contact Us
What is Hamstring Strain ?
- Home
- What is Hamstring Strain ?
What is Hamstring Strain ?
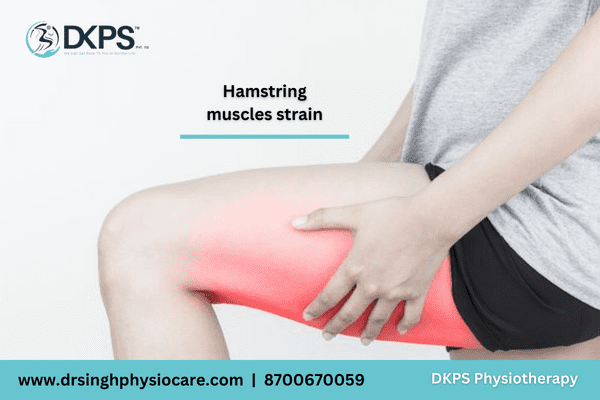
Definition:
Hamstring pain refers to discomfort or injury affecting the group of muscles located at the back of the thigh. These muscles play a crucial role in activities like walking, running, and jumping, making hamstring pain a common complaint among athletes and individuals leading active lifestyles. Understanding its causes, symptoms, diagnosis, and treatment options is essential for effective management.
Causes:
1. Muscle Strain: One of the primary causes of hamstring pain is a strain or tear in the hamstring muscles. This often occurs due to sudden movements, overstretching, or inadequate warm-up before physical activity.
2. Overuse: Continuous stress on the hamstring muscles without sufficient rest can lead to overuse injuries, resulting in pain and discomfort.
3. Poor Flexibility: Tightness in the hamstring muscles due to inadequate stretching or poor flexibility can increase the risk of injury.
4. Muscle Imbalance: Weakness or imbalance between the hamstring and opposing muscle groups (quadriceps) can also contribute to hamstring pain.
5. Direct Trauma: Direct impact or trauma to the back of the thigh can cause bruising or injury to the hamstring muscles.
Signs and Symptoms:
1. Pain: Pain or discomfort in the back of the thigh, which may range from mild to severe depending on the extent of the injury.
2. Swelling: Swelling or inflammation in the affected area.
3. Tenderness: Tenderness to touch over the hamstring muscles.
4. Reduced Range of Motion: Difficulty in extending the leg or bending at the knee.
5. Weakness: Weakness or instability while walking or performing activities that involve the use of the hamstring muscles.
Examination and Investigation:
1. Physical Examination: A thorough physical examination by a healthcare professional can help assess the severity of the injury, identify areas of tenderness, and evaluate range of motion.
2. Imaging Studies: In some cases, imaging studies such as ultrasound, MRI, or CT scans may be recommended to visualize the extent of muscle damage or rule out other underlying conditions.
Diagnosis:
Based on the clinical evaluation and imaging findings, a diagnosis of hamstring injury can be made. The severity of the injury is often categorized as mild, moderate, or severe, depending on the extent of muscle involvement and associated symptoms.
Treatment:
1. Rest and Ice: Initial treatment typically involves rest, ice application, compression, and elevation (RICE protocol) to reduce pain and inflammation.
2. Pain Management: Over-the-counter pain medications may be prescribed to alleviate pain and discomfort.
3. Physical Therapy: A structured physical therapy program focusing on stretching, strengthening, and flexibility exercises can help improve muscle function and prevent future injuries.
4. Gradual Return to Activity: Gradually reintroducing physical activity and sports-specific exercises under the guidance of a healthcare professional can facilitate recovery and prevent re-injury.
Physiotherapy Treatment:
DKPS physiotherapy offers personalized physiotherapy treatment plans tailored to the individual needs of patients with hamstring injuries. Their team of experienced physiotherapists utilizes a variety of techniques, including manual therapy, therapeutic exercises, ultrasound, and electrical stimulation, to promote healing and restore function.
Conclusion:
Hamstring pain can significantly impact daily activities and sports performance if left untreated. By understanding its causes, symptoms, and treatment options, individuals can take proactive steps to manage and prevent hamstring injuries. Seeking prompt medical attention and enrolling in a comprehensive rehabilitation program, such as those offered by DKPS physiotherapy, can facilitate a speedy recovery and reduce the risk of recurrence.
Other Places where we provide Physiotherapy Services at Home
- Physiotherapy at home in Rohini sector 24
- Physiotherapy at home in Rohini
- Physiotherapy at home in Budh vihar
- Physiotherapy at home in pitampura
- Physiotherapy at home in Panjabi bagh
- Physiotherapy at home in Rani bagh
- Physiotherapy at home in Ashok vihar
- Physiotherapy at home in shastri nagar Delhi
- Physiotherapy at home in inderlok Delhi
- Physiotherapy at home in kanhaiya Nagar Delhi
- Physiotherapy at home in paschim vihar
- Physiotherapy at home in Vikas Puri
- Physiotherapy at home in Karol bagh
- Physiotherapy at home in Rajendra place delhi
- Physiotherapy at home in Patel Nagar Delhi
- Physiotherapy at home in Shadipur delhi
- Physiotherapy at home in Kirti Nagar Delhi
- Physiotherapy at home in moti nagar Delhi
- Physiotherapy at home in Noida
- Physiotherapy at home in Gaziyabad
- Physiotherapy at home in Gurgaon
- Physiotherapy at home in Faridabad
- Physiotherapy at home in burari
- Physiotherapy at home in sangam vihar
- Physiotherapy at home in Gandhi vihar
- Physiotherapy at home in mukherjee nagar
- Physiotherapy at home in jagatpur village
- Physiotherapy at home in gopalpur
- Physiotherapy at home in civil line
- Physiotherapy at home in delhi university
- Physiotherapy at home in Mumbai
- Physiotherapy at home in GTB nagar
- Physiotherapy at home in model town
- Physiotherapy at home in kamla nagar
- Physiotherapy at home in nirankari colony
- Physiotherapy at home in Chauhanpatti
- Physiotherapy at home at khjuri khas
- Physiotherapy at home in Bhajanpura
- Physiotherapy at home in Ankur vihar
- Physiotherapy at home in tronica city
- Physiotherapy at home in Jhaghirpuri
- Physiotherapy at home in Okhla delhi
- Physiotherapy at home in shaeen bagh delhi
- Physiotherapy at home in houz khash Delhi
- Physiotherapy at home in Narela delhi
Find Complete Relief from Dr. Singh Physiocare Experts
If you think you are looking for similar services like Physiotherapist in Mumbai, Lucknow, Delhi, NCR, or Physiotherapy at Home Near Me,
please contact Dr. Singh Physiocare, team to schedule an appointment at : 8700670059 or 9953024412
Book You Appointment Today:
Additional Links
For More Articles
DKPS Physiotherapy services at Home
DWARKA | PASCHIM VIHAR | PEERAGARHI | VIKASPURI | PITAMPURA | KOHAT ENCLAVE | RANI BAGH | ROHINI | JANAKPURI | MANGOLPURI | PUNJABI BAGH | NANGLOI | BAHADURGARH | NOIDA | GREATER NOIDA| GHAZIABAD | GURGAON | FARIDABAD | MUMBAI | GORAKHPUR | LUCKNOW | CHANDIGARH |
